Everything You Need to Know About Chlamydia Infection
Chlamydia infection is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. It is one of the most common STIs in the United States, and it is particularly prevalent among young people, especially women.
Chlamydia infection is primarily spread through vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected partner. In some cases, it can also be spread from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth.
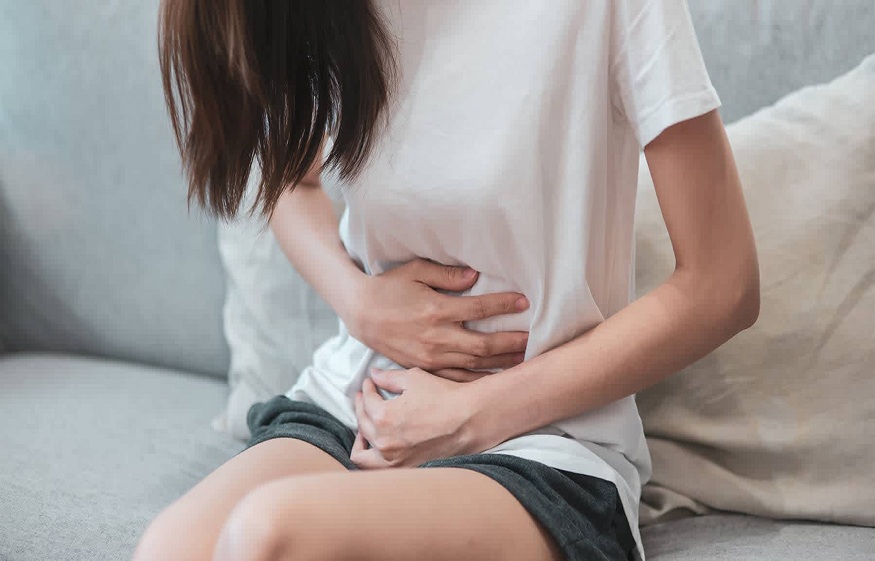
Symptoms of Chlamydia infection can range from mild to severe and may include:
- Discharge from the vagina or penis
- Painful urination
- Pain during sex
- Abdominal pain
- Pain in the lower back or pelvis
In many cases, Chlamydia infection is asymptomatic, meaning that it does not cause any noticeable symptoms. As a result, many people with the infection may not be aware that they have it, and they may unknowingly spread the infection to others.
Diagnosis of Chlamydia infection typically involves a simple test, such as a urine test or a swab test of the vagina or anus, to detect the presence of the bacteria.
Treatment for Chlamydia infection typically involves a course of antibiotics, such as azithromycin or doxycycline, to kill the bacteria and clear the infection. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as directed, even if symptoms resolve before the end of treatment, to ensure that the infection is fully treated.
In addition to treatment, it is important for individuals with Chlamydia infection to inform their sexual partners and to practice safe sex, such as using condoms, to prevent the spread of the infection.
In conclusion, Chlamydia infection is a common STI caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. It is primarily spread through vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected partner and can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe. Diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics are important to clear the infection and prevent the spread of the disease.
Certainly, here is an example to illustrate the evaluation and treatment of Chlamydia infection:
A 25-year-old female patient presents to the clinic with complaints of vaginal discharge and painful urination. Further evaluation reveals that the patient is sexually active and reports having unprotected sexual intercourse with a new partner in the past month.
Based on the patient’s symptoms and sexual history, the healthcare provider performs a swab test of the vagina to test for Chlamydia infection. The results of the test are positive for the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.
The healthcare provider diagnoses the patient with Chlamydia infection and prescribes a course of azithromycin to clear the infection. The patient is instructed to take the antibiotics as directed and to return for a follow-up appointment in one week to ensure that the infection has been fully treated.
The patient is also advised to inform her sexual partners of the infection and to practice safe sex, such as using condoms, to prevent the spread of the infection.
In this example, the patient’s symptoms of vaginal discharge and painful urination are evaluated and diagnosed as Chlamydia infection. The healthcare provider emphasizes the importance of prompt treatment with antibiotics to clear the infection and prevent the spread of the disease, as well as the importance of safe sex practices to reduce the risk of future infections.